How to Install an Exterior Door
Exterior doors are most often replaced due to poor preparation when the door was installed. When installed properly an exterior door should last many decades. As with any project, it's best to take your time and understand the project before you start.
Preparation:
Installing a simple exterior door does not take more than a few hours of labor for most, but you will want at least a couple days for the preparation.
Measure:
Accurate measurements is very important and will reduce the installation time. I like to measure the rough opening and not the inside of the door jamb. This will eliminate any measurement errors that the old door may have. For example if the old door was too small and used excessive shims then the new door will need excessive shims. Also when you measure from 2x4 to 2x4 you can check the frame for rot. If you they need replacing, make sure you have them before your project is started.
The easiest way to measure the rough opening is to pull the trim molding from the inside of the door. To pull the trim you will need a razor knife, hammer and pry bar. If there is any paint build up, use the razor knife score along the edge where the trim meets the drywall, with the razor knife angled towards the trim. Then use the pry bar to pry off the trim.
With the trim molding removed you should be able to see the rough opening 2x4 and the amount of shims used for the old door. To get an accurate measurement you can insert two shims (on each side of the doorway) and place them between the door jamb and 2x4 frame. Then measure from shim to shim. This will give you the rough opening width. You will want to do this for the top, middle, and bottom. Once you have all three measurement you can order the door. Most common exterior single door is 36 inch and is usually in stock at most big box stores.f
Painting (Very Important!) :
A pre-hung door looks like you just install it, that is not the case. You must first prep the door, the door warranty is only valid if you follow the manufacturers instructions. In most cases the door jambs and door edges are primed white, do not confuse this with paint.
Removing the old door.
Before removing the old door, make sure you have everything ready. Make a check list of everything you need. Once you have the old door removed you do not want to have to run around looking for the things you need.
At minimum you will need:
Preparing the rough opening.
Once the door is out, you will need a closer inspection of the 2x4 frame. And replace them if you see any rot. (If you noticed any rot when you where measuring the rough opening, you should have replacement 2x4s ready (always use pressure treated lumber (they usually have a greenish color) ))
If the frame is in good shape you will need to use the level to check the floor and side for level. If the floor is not level you will need to make it as level as possible. By filling in the low spots or removing the high spots.
Door Installation
Now that you have the hard parts done, the door should go up easy. Making sure the floor is clean and free from dust, dirt, etc. Place the door face down with the threshold just outside of the rough opening. Add silicon caulking to the bottom of the door and stand up the pre-hung door in to place.
Next open the door placing scrape wood or other type of supports under the door. And adjust the supports to hold the door jamb in place. Staring at the top, make the door jamb flush with the inside (where the inside trim is attached) and add the shims equally on both sides. I start at the top since the top shims offer the most support. If you are working by yourself you tack in the top on the hinge side to help hold the door in place. Then add the shims to the middle and then the bottom and check the side for level. Make sure the door jamb is flush with the inside wall as you work your way down the door. You may have to adjust the shims. Remember that you will have two options for each adjustment. You can achieve the same adjustment by moving the top or the bottom in opposite direction. You should always choose to adjust the top or bottom based on how much wiggle room you have. If the top has the most wiggle room then adjust the top. Once you have the door jamb level add four screws, two on each side (near the top and bottom).
Now the door should stay up without any support. And it's time to test it, gently close the shut and make sure that you have ample clearance (about 1/4 inch but check the door instructions). Some doors come with a little nob to indicate the required clearance. If you need to make an adjustment remove one screw and adjust the shim. If a minor adjustment is needed you can simple tighten a screw to pull the jamb in the that direction. Once the you have the adjustments finished, you can add two more screws to each side in the middle. Be careful not to bow the door jamb, by tightening the screw too much.
Now test the door, if no other adjustments are needed you can add the 2 1/2 screws to the hinges. Most door will have one open hole on each hinge. Simple drive the screw through the door jamb and into the 2x4 frame. Now the door is installed and ready for hardware and trim.
Extension for a Storm Door or Brick Molding.
If you want to install a storm door or have walls greater than 6 inches then an door extension is what you will want. The big box store will have these in stock, but if you have the tools they are very simple to make.
Making an exterior door extension.
You will need three pieces a top and two sides. I use Google Sketch It to draw out anything I build and have taken a 2-D picture from the drawing.
This was for an older home and most everything needed to be custom. From the image you can see that the storm door requires 35 3/4 inch width and I made the sides a little log so I can cut each one to fit.
To find the measurements:
Now take the width of the doorway (38 3/4) and subtract the width required for the storm door (35 3/4), which comes out to 3 inches. Since there are two side divided by 2. This will give you the width of the side at 1 1/2 inches wide.
Top:
The top is the same width of the two sides. But the height you will need to calculate; Subtract the height required for the storm door from the height of the doorway. In this example the doorway was 82 1/4 and the door was adjustable, but the door was to set at the minimum of 78 3/4. (Height = 82 1/4 - 78 3/4 = 3 1/2). So the dimension of the top is 38 3/4 wide, 3 1/2 high, 1 1/2 thick.
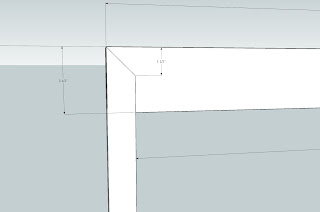 Since the height of the top was taller than the width of the side, a simple 45 degree cut would not do. By using Google Sketch Up I can calculate the length of each cut. But it's not very hard to figure out. If you can not cut a a simple 45 on each piece and need to make a cut similar to this example. Using a table saw, raise the blade to the top width - side width (3 1/2 - 1 1/2 = 2) of the side and mark each end of the top, 2 inches in. So you would have to marks 2 inches for both end. Now pass each end making a 2 inch deep cut 1 1/2 inches in. Then tilt the blade to a 45 degree and turn over the top. Line up the bottom of the blade with the corner of the top end, adjust the blade to where you can just see the blade through the 1 1/2 cut you just made. Then make the cut on each end. If you think you might I trouble making this type of cut you should use a scrape piece of wood the same width and thickness of the top member. The straight cut will be simple but the angle cut is more difficult. Once you have the angle correct you can cut the angles on the top member and then make the straight cut.
Since the height of the top was taller than the width of the side, a simple 45 degree cut would not do. By using Google Sketch Up I can calculate the length of each cut. But it's not very hard to figure out. If you can not cut a a simple 45 on each piece and need to make a cut similar to this example. Using a table saw, raise the blade to the top width - side width (3 1/2 - 1 1/2 = 2) of the side and mark each end of the top, 2 inches in. So you would have to marks 2 inches for both end. Now pass each end making a 2 inch deep cut 1 1/2 inches in. Then tilt the blade to a 45 degree and turn over the top. Line up the bottom of the blade with the corner of the top end, adjust the blade to where you can just see the blade through the 1 1/2 cut you just made. Then make the cut on each end. If you think you might I trouble making this type of cut you should use a scrape piece of wood the same width and thickness of the top member. The straight cut will be simple but the angle cut is more difficult. Once you have the angle correct you can cut the angles on the top member and then make the straight cut.
Brick Molding Installation:
Once you have everything cut it's ready to be installed. You have two choices the first is to nail or screw the molding in to the exterior door jamb. Or you can screw it in to the inside of the doorway. If the brick molding lines up nicely with the door jamb (in most cases it will) the nail or screw it to the door jamb. Once you have the extension (brick molding) up your ready to hang the storm door. Since this varies from door to you should follow the manufactures installation guide (reading and understanding it first then start the installation).
As always, do not rush the project, take your time and think about how each step will effect other aspects of the project. There is nothing worse than having to deconstruct something you just built.
Preparation:
Installing a simple exterior door does not take more than a few hours of labor for most, but you will want at least a couple days for the preparation.
Measure:
Accurate measurements is very important and will reduce the installation time. I like to measure the rough opening and not the inside of the door jamb. This will eliminate any measurement errors that the old door may have. For example if the old door was too small and used excessive shims then the new door will need excessive shims. Also when you measure from 2x4 to 2x4 you can check the frame for rot. If you they need replacing, make sure you have them before your project is started.
The easiest way to measure the rough opening is to pull the trim molding from the inside of the door. To pull the trim you will need a razor knife, hammer and pry bar. If there is any paint build up, use the razor knife score along the edge where the trim meets the drywall, with the razor knife angled towards the trim. Then use the pry bar to pry off the trim.
With the trim molding removed you should be able to see the rough opening 2x4 and the amount of shims used for the old door. To get an accurate measurement you can insert two shims (on each side of the doorway) and place them between the door jamb and 2x4 frame. Then measure from shim to shim. This will give you the rough opening width. You will want to do this for the top, middle, and bottom. Once you have all three measurement you can order the door. Most common exterior single door is 36 inch and is usually in stock at most big box stores.f
Painting (Very Important!) :
A pre-hung door looks like you just install it, that is not the case. You must first prep the door, the door warranty is only valid if you follow the manufacturers instructions. In most cases the door jambs and door edges are primed white, do not confuse this with paint.
Primer is porous and will absorb moisture like paint or water, left unpainted the jambs will more than likely rot out in a couple of years.Most fiberglass door have no wood and the door edges will not need to be painted, but the door jambs are wood and will need to be painted. On most steel doors with a wood core will need the sides (edges) of the door and jambs painted and solid wood doors may come completely finished or unfinished. Any part that you have to paint, make sure you paint two coats. Waiting at least 4 hours between coats. Make sure to follow your manufactures preparation guide or it may void your warranty.
Removing the old door.
Before removing the old door, make sure you have everything ready. Make a check list of everything you need. Once you have the old door removed you do not want to have to run around looking for the things you need.
At minimum you will need:
- Level to check the rough opening.
- Hammer, Chisel and/or grinder.
- Nails or screws or Nail gun.
- Caulking and caulking gun.
- Broom and hand brush or vacuum.
- Screw drivers and pry bar.
- Cordless drill and any bits you will need.
- Rags, clean water, gloves and a bucket for trash. (clean as you go!)
- Scrape wood.
Preparing the rough opening.
Once the door is out, you will need a closer inspection of the 2x4 frame. And replace them if you see any rot. (If you noticed any rot when you where measuring the rough opening, you should have replacement 2x4s ready (always use pressure treated lumber (they usually have a greenish color) ))
If the frame is in good shape you will need to use the level to check the floor and side for level. If the floor is not level you will need to make it as level as possible. By filling in the low spots or removing the high spots.
Door Installation
Now that you have the hard parts done, the door should go up easy. Making sure the floor is clean and free from dust, dirt, etc. Place the door face down with the threshold just outside of the rough opening. Add silicon caulking to the bottom of the door and stand up the pre-hung door in to place.
Next open the door placing scrape wood or other type of supports under the door. And adjust the supports to hold the door jamb in place. Staring at the top, make the door jamb flush with the inside (where the inside trim is attached) and add the shims equally on both sides. I start at the top since the top shims offer the most support. If you are working by yourself you tack in the top on the hinge side to help hold the door in place. Then add the shims to the middle and then the bottom and check the side for level. Make sure the door jamb is flush with the inside wall as you work your way down the door. You may have to adjust the shims. Remember that you will have two options for each adjustment. You can achieve the same adjustment by moving the top or the bottom in opposite direction. You should always choose to adjust the top or bottom based on how much wiggle room you have. If the top has the most wiggle room then adjust the top. Once you have the door jamb level add four screws, two on each side (near the top and bottom).
Now the door should stay up without any support. And it's time to test it, gently close the shut and make sure that you have ample clearance (about 1/4 inch but check the door instructions). Some doors come with a little nob to indicate the required clearance. If you need to make an adjustment remove one screw and adjust the shim. If a minor adjustment is needed you can simple tighten a screw to pull the jamb in the that direction. Once the you have the adjustments finished, you can add two more screws to each side in the middle. Be careful not to bow the door jamb, by tightening the screw too much.
Now test the door, if no other adjustments are needed you can add the 2 1/2 screws to the hinges. Most door will have one open hole on each hinge. Simple drive the screw through the door jamb and into the 2x4 frame. Now the door is installed and ready for hardware and trim.
Extension for a Storm Door or Brick Molding.
If you want to install a storm door or have walls greater than 6 inches then an door extension is what you will want. The big box store will have these in stock, but if you have the tools they are very simple to make.
Making an exterior door extension.
You will need three pieces a top and two sides. I use Google Sketch It to draw out anything I build and have taken a 2-D picture from the drawing.
This was for an older home and most everything needed to be custom. From the image you can see that the storm door requires 35 3/4 inch width and I made the sides a little log so I can cut each one to fit.
To find the measurements:
- The manufacture of the storm door will have the required width. In this example it was 35 3/4 inch.
- Also you will need the height of the storm door, many are adjustable.
- Measure from the threshold to the top of the doorway. In this example it was 82 1/4.
- Measure the width of the doorway. In this example it was 38 3/4.
Now take the width of the doorway (38 3/4) and subtract the width required for the storm door (35 3/4), which comes out to 3 inches. Since there are two side divided by 2. This will give you the width of the side at 1 1/2 inches wide.
Top:
The top is the same width of the two sides. But the height you will need to calculate; Subtract the height required for the storm door from the height of the doorway. In this example the doorway was 82 1/4 and the door was adjustable, but the door was to set at the minimum of 78 3/4. (Height = 82 1/4 - 78 3/4 = 3 1/2). So the dimension of the top is 38 3/4 wide, 3 1/2 high, 1 1/2 thick.
 Since the height of the top was taller than the width of the side, a simple 45 degree cut would not do. By using Google Sketch Up I can calculate the length of each cut. But it's not very hard to figure out. If you can not cut a a simple 45 on each piece and need to make a cut similar to this example. Using a table saw, raise the blade to the top width - side width (3 1/2 - 1 1/2 = 2) of the side and mark each end of the top, 2 inches in. So you would have to marks 2 inches for both end. Now pass each end making a 2 inch deep cut 1 1/2 inches in. Then tilt the blade to a 45 degree and turn over the top. Line up the bottom of the blade with the corner of the top end, adjust the blade to where you can just see the blade through the 1 1/2 cut you just made. Then make the cut on each end. If you think you might I trouble making this type of cut you should use a scrape piece of wood the same width and thickness of the top member. The straight cut will be simple but the angle cut is more difficult. Once you have the angle correct you can cut the angles on the top member and then make the straight cut.
Since the height of the top was taller than the width of the side, a simple 45 degree cut would not do. By using Google Sketch Up I can calculate the length of each cut. But it's not very hard to figure out. If you can not cut a a simple 45 on each piece and need to make a cut similar to this example. Using a table saw, raise the blade to the top width - side width (3 1/2 - 1 1/2 = 2) of the side and mark each end of the top, 2 inches in. So you would have to marks 2 inches for both end. Now pass each end making a 2 inch deep cut 1 1/2 inches in. Then tilt the blade to a 45 degree and turn over the top. Line up the bottom of the blade with the corner of the top end, adjust the blade to where you can just see the blade through the 1 1/2 cut you just made. Then make the cut on each end. If you think you might I trouble making this type of cut you should use a scrape piece of wood the same width and thickness of the top member. The straight cut will be simple but the angle cut is more difficult. Once you have the angle correct you can cut the angles on the top member and then make the straight cut.Brick Molding Installation:
Once you have everything cut it's ready to be installed. You have two choices the first is to nail or screw the molding in to the exterior door jamb. Or you can screw it in to the inside of the doorway. If the brick molding lines up nicely with the door jamb (in most cases it will) the nail or screw it to the door jamb. Once you have the extension (brick molding) up your ready to hang the storm door. Since this varies from door to you should follow the manufactures installation guide (reading and understanding it first then start the installation).
As always, do not rush the project, take your time and think about how each step will effect other aspects of the project. There is nothing worse than having to deconstruct something you just built.
Labels: brick molding, DIY, DIY door installation, Door Extension, door installation, door jambs, Exterior Door













